Protecting your skin from the harmful UV rays of the sun is crucial. Proper sun protection can reduce your risk of sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer, whether you’re spending a day at the beach or walking outside casually. While sunscreen and sunblock are essential tools in this effort, they are not the only ones. Protective clothes, such as long-sleeved shirts, seek shade; remember to avoid direct sun exposure during peak hours. They are also essential. But should you choose sunscreen or sunblock when it comes to sun protection?
Let’s delve into the differences between sunscreen and sunblock, empowering you to make the best choice for your unique skin.
Overview of Sunscreen and Sunblock
- Sunscreen: Acts like a chemical filter that absorbs UV rays before they penetrate your skin.
- Sunblock: Creates a physical barrier that reflects and blocks UV rays from reaching your skin.
Differences Between Sunscreen and Sunblock
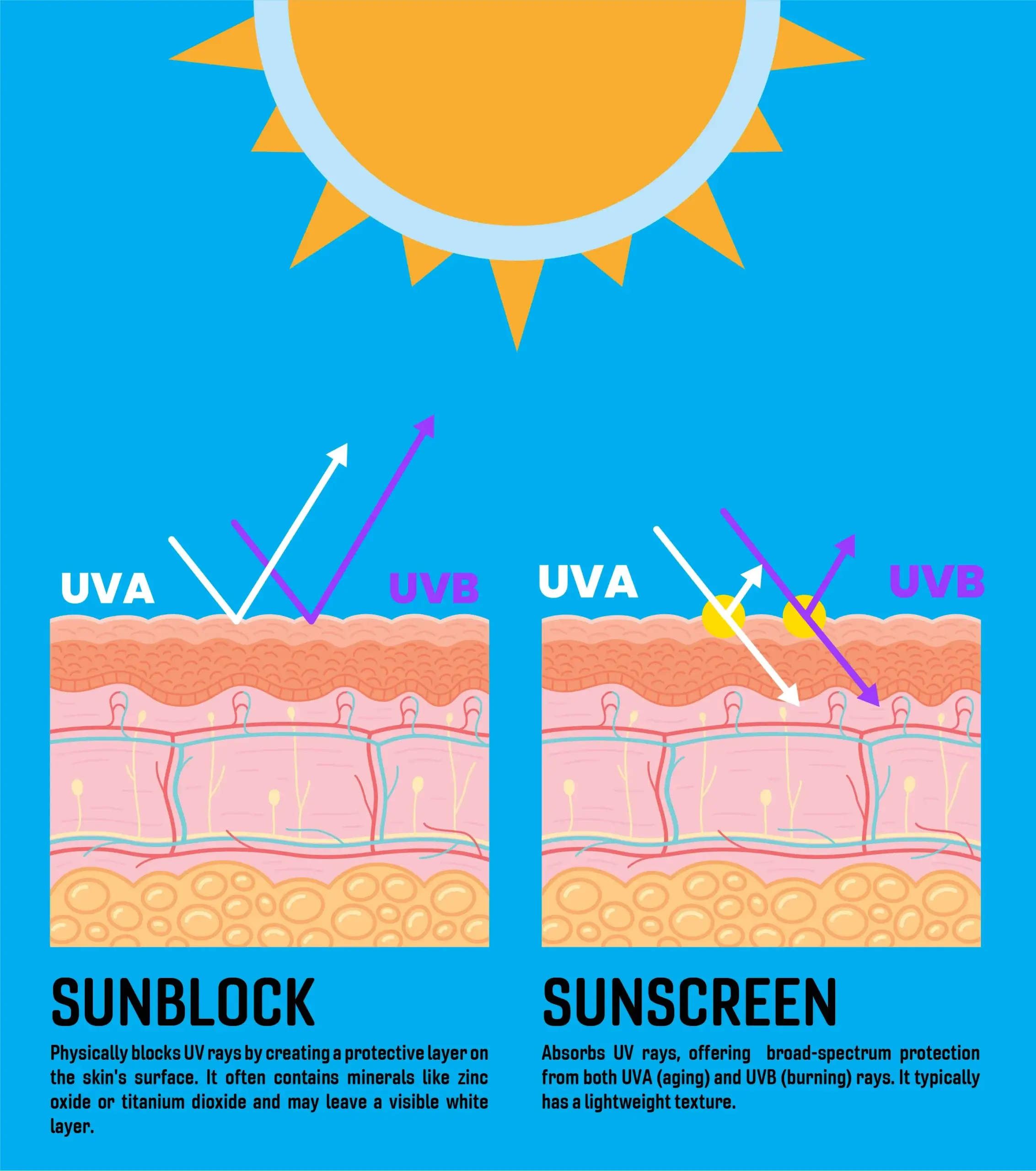
The primary difference between sunscreen and sunblock lies in how they interact with UV rays:
- Sunscreen: Absorbs UV rays, offering broad-spectrum protection from both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays. It typically has a lightweight texture.
- Sunblock: Physically blocks UV rays by creating a protective layer on the skin’s surface. It often contains minerals like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide and may leave a visible white layer.
Ingredients in Sunscreen
Sunscreen usually contains a combination of chemicals that provide UV protection:
- Avobenzone: Prot ects against UVA rays.
- Octyl Methoxycinnamate: Absorbs UVB rays.
- Oxybenzone: Offers broad-spectrum protection.
- Homosalate and Octisalate: Enhance UVB protection.
Ingredients in Sunblock
Sunblock relies on natural minerals that physically block UV rays:
- Zinc Oxide: Offers broad-spectrum protection.
- Titanium Dioxide: Reflects UVB rays and some UVA rays.
Application and Usage
- Sunscreen: Apply 20-30 minutes before sun exposure. Reapply every two hours or after swimming.
- Sunblock: Works immediately after application. Reapply every two hours or after swimming.
Suitability for Different Skin Types

- Sensitive Skin: Sunblock is better due to its mineral ingredients, which are less likely to cause irritation.
- Acne-Prone Skin: Look for non-comedogenic sunscreen to avoid clogging pores.
- Dry Skin: Sunscreen with moisturizing ingredients is ideal.
- Oily Skin: Opt for lightweight, oil-free sunscreen or sunblock.
Which One is More Effective?
Both sunscreen and sunblock are effective when used correctly. The best option depends on your skin type, preferences, and lifestyle:
- Sunscreen: Ideal for daily use due to its lightweight feel and invisibility.
- Sunblock: Perfect for extended outdoor activities because of its robust protection.




